what is the physiological function of gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis porcess, steps & pathway
Gluconeogenesis, although it may sound like a complex biochemical process, is an essential pathway that takes place in our bodies to maintain blood glucose levels. Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating process that keeps us fueled and energized!
Pin on Biochemistry Cycles
 In our journey of understanding gluconeogenesis, let’s start with a picturesque representation of the biochemistry cycles. The image above provides a visual overview of various interconnected cycles related to metabolism.
In our journey of understanding gluconeogenesis, let’s start with a picturesque representation of the biochemistry cycles. The image above provides a visual overview of various interconnected cycles related to metabolism.
Gluconeogenesis, as the name suggests, is the process of generating new glucose molecules. These glucose molecules are synthesized in our bodies primarily in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys. This metabolic pathway is crucial because it allows us to produce glucose even when the dietary intake of carbohydrates is insufficient. Therefore, gluconeogenesis plays a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels, which is essential for the proper functioning of our brain and muscles.
Gluconeogenesis Process, Steps & Pathway
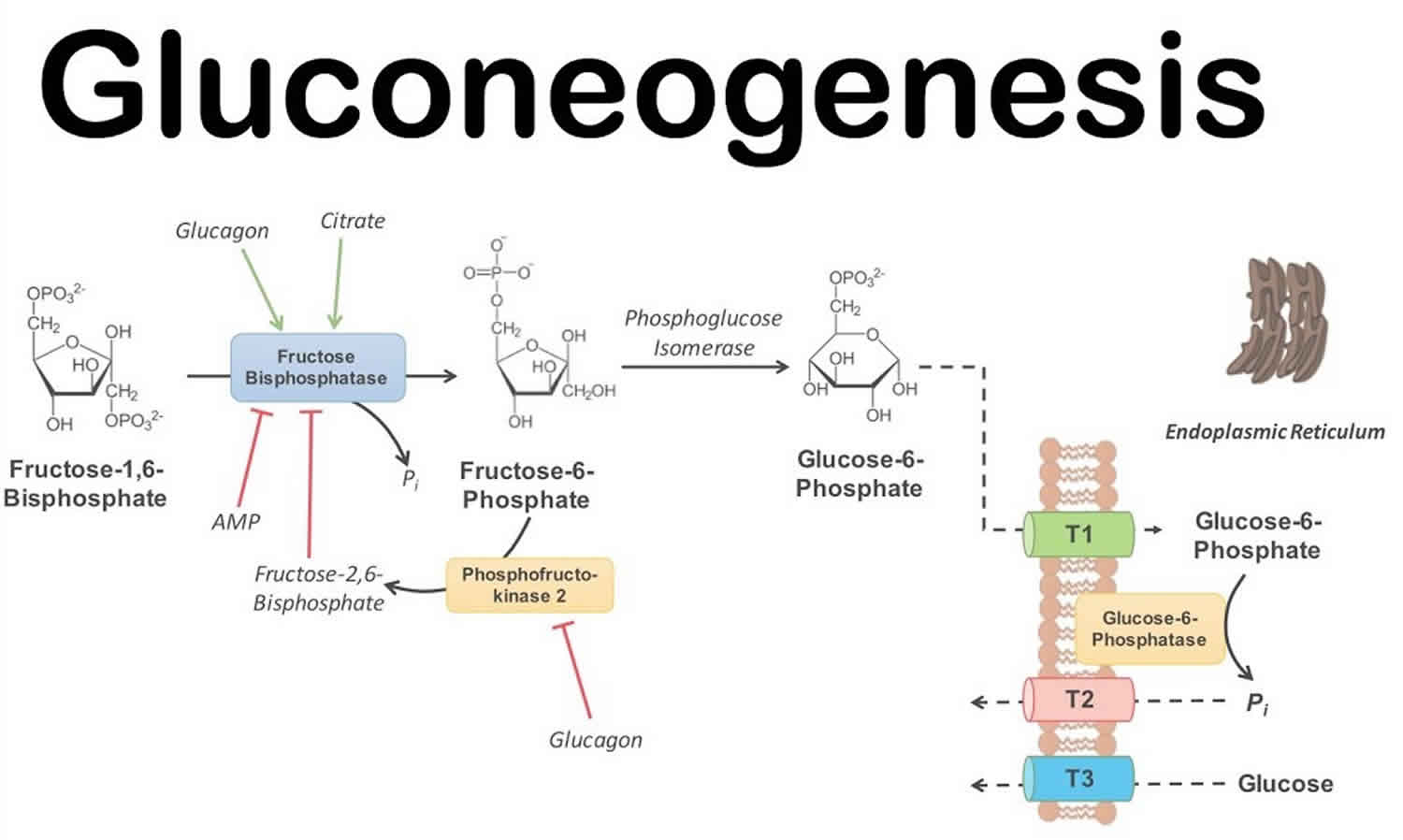 The image above illustrates the detailed steps involved in the gluconeogenesis pathway. Let’s break it down:
The image above illustrates the detailed steps involved in the gluconeogenesis pathway. Let’s break it down:
1. The process starts with molecules such as lactate, pyruvate, and certain amino acids, which are converted into oxaloacetate.
2. Oxaloacetate is then converted into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), a key intermediate in the gluconeogenesis pathway.
3. PEP is further converted into glucose-6-phosphate, which can be readily converted into glucose. This step involves the activity of various enzymes and metabolic reactions.
In general, gluconeogenesis involves a series of enzymatic reactions that ultimately lead to the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. This process requires energy and consumes ATP (adenosine triphosphate) in multiple steps.
Now, you might be wondering when and why gluconeogenesis becomes significant. Well, during situations like prolonged fasting, intense exercise, or consuming a low-carbohydrate diet, our body turns to gluconeogenesis to maintain adequate blood glucose levels. This metabolic adaptation ensures that organs and tissues relying on glucose, such as the brain and red blood cells, receive a constant supply of this vital energy source.
Understanding gluconeogenesis sheds light on the remarkable adaptability and resilience of our bodies. It showcases the intricate biochemical mechanisms that operate to maintain our overall well-being even under challenging conditions.
So, the next time you hear about gluconeogenesis, you can now appreciate its significance in keeping us energized and functioning optimally. Here’s to the amazing intricacies of our biochemistry!
If you are searching about Which Of The Following Can Be Precursors To Gluconeogenesis - slideshare you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pics about Which Of The Following Can Be Precursors To Gluconeogenesis - slideshare like Pin on Biochemistry Cycles, Gluconeogenesis porcess, steps & pathway and also What is gluconeogenesis - physiological function, key enzymes. Here you go:
Which Of The Following Can Be Precursors To Gluconeogenesis - Slideshare
 slideinshare.blogspot.comgluconeogenesis pathway glycolysis regulation allosteric
slideinshare.blogspot.comgluconeogenesis pathway glycolysis regulation allosteric
Gluconeogenesis Porcess, Steps & Pathway
 healthjade.netgluconeogenesis regulation steps glucose pathway blood kidney glycerol function contents which
healthjade.netgluconeogenesis regulation steps glucose pathway blood kidney glycerol function contents which
What Is Gluconeogenesis - Physiological Function, Key Enzymes
 biology.reachingfordreams.comgluconeogenesis steps enzymes pathway substrates glycolysis key many biology utilizes but
biology.reachingfordreams.comgluconeogenesis steps enzymes pathway substrates glycolysis key many biology utilizes but
Pin On Biochemistry Cycles
 www.pinterest.deglycolysis gluconeogenesis pathways diagram pathway steps enzymes biology gluconeogenic glycolytic simple notes pyruvate reverse biochemistry step process respiration cellular important
www.pinterest.deglycolysis gluconeogenesis pathways diagram pathway steps enzymes biology gluconeogenic glycolytic simple notes pyruvate reverse biochemistry step process respiration cellular important
Gluconeogenesis- Steps, Reactions And Significance
 microbenotes.comgluconeogenesis significance
microbenotes.comgluconeogenesis significance
Pin on biochemistry cycles. Gluconeogenesis pathway glycolysis regulation allosteric. Gluconeogenesis significance